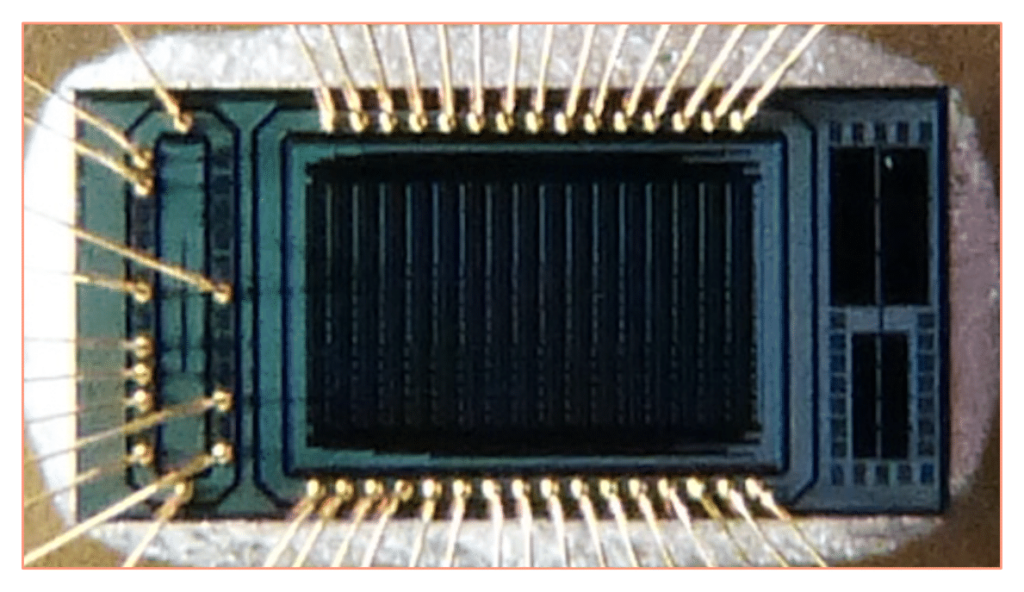
Single photon avalanche diodes can guarantee state-of-the-art space and time resolution in capturing weak optical signals while covering quite a large set of applications. In relatively recent times, CMOS SPAD technologies have been emerging as an extremely flexible solution for the design of sensor arrays with monolithically integrated processing electronics. The group at EIL has been working on the design and characterization of low-noise CMOS SPADs for charged particle tracking based on vertically interconnected arrays of sensors. The first prototype of a two-tier SPAD detector, providing a coincidence signal when a particle simultaneously strikes two overlapping sensors, was fabricated in a commercial 150 nm process and successfully tested. This solution leads to a strong reduction of the dark count rate (DCR), as the rate of coincidence signals generated by concurrent random dark current pulses occurring in two overlapping pixels can be made a small fraction of the DCR from each individual sensor, depending on the duration of the coincidence window.